
If you're trying to decide between casting and forging for your stainless steel application, the table below will help guide your choice. It outlines the key factors that influence the decision, so you can choose the most suitable process for your needs.
Table of contents
- Difference Between SS Forging vs Casting
- Stainless Steel Casting Process
- Reasons to Choose Forging and Casting
- SS 304 Castings Applications
- Advantages of SS Investment Casting
- Stainless Steel Cast Grades and Composition
- ASTM A351 CF8M Cast Fittings Testing Methods
- Types of Stainless Steel Pressure Die Casting Processes
- Methods Used for Stainless Steel 316 Casting
- SS Investment Casting vs Sand Casting
Understanding the Difference Between Stainless Steel Forging and Casting
Choosing between forging and casting depends on several factors such as design complexity, mechanical properties, cost, and application requirements. The table below highlights the main differences between the two processes.
Difference Between SS Forging vs Casting
| Features | Stainless Steel Casting | Stainless Steel Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Casting involves melting metal and pouring it into a mold. | Forging shapes solid metal using pressure or hammering. |
| Product Size | Limited by mold size and thickness. | Can produce a wide range of sizes. |
| Shape Complexity | Best for intricate and detailed parts. | More suitable for simpler shapes. |
| Tolerance | Less precise in complex geometries. | Offers tighter tolerances and better accuracy. |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste due to precision. | Higher material loss from trimming and cutting. |
| Strength | Lower tensile and impact strength. | Higher strength and durability. |
| Surface Finish | Rougher finish, requires post-processing. | Better surface quality, often ready for use. |
| Cost | More cost-effective for small to medium runs. | Higher initial costs but efficient for mass production. |
| Internal Defects | More prone to porosity and shrinkage. | Generally fewer internal defects, better material integrity. |
| Applications | Used for pump housings, valve bodies, etc. | Preferred for structural components and high-strength parts. |
Overview of the Stainless Steel Precision Casting and Forging Process
Whether you're looking to cast or forge stainless steel, understanding the process is crucial. Below is a detailed explanation of how each method works, helping you make an informed decision based on your project's needs.
Stainless Steel Casting Process

Step-by-step Process of Stainless Steel Casting
Step 1: Pattern Making
Patterns are made from wax, plastic, wood, or foam, serving as a replica of the final product in investment casting.
- Wax patterns
- Plastic patterns
- Wooden patterns
- Foam patterns
- Metal patterns
Step 2: Casting Process
This includes various methods like sand casting, shell mold casting, and investment casting:
- Shell Mold Casting: Produces thin-walled molds with high dimensional accuracy.
- Ceramic Mold Casting: Offers excellent surface finish and precise dimensions.
Step 3: Melting and Pouring
- Melt the metal in an electric arc furnace.
- Pour the molten metal into the mold carefully to avoid damaging the mold.
Step 4: Finishing
- Remove residual mold material (sand or ceramic).
- Perform cleaning and finishing operations like grinding, polishing, or machining.
Top 5 Reasons to Choose Forging and Casting
Both forging and casting have their own advantages, making them suitable for different applications. Here are the top reasons why you might choose one over the other:
Reasons to Choose Forging and Casting
| Forging | Casting |
|---|---|
|
|
Applications of Stainless Steel Forged and Cast Products
Stainless steel forged and cast products are widely used across industries due to their strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Some common applications include:
SS 304 Castings Applications
- Oil and gas industry
- Construction and architecture
- Power generation
- Food processing equipment
- Automotive components
- Chemical and pharmaceutical equipment
- Medical devices
- Kitchenware and cutlery

Advantages of SS Investment Casting

- Excellent heat resistance
- High durability and long service life
- Corrosion-resistant
- Environmentally friendly
- Recyclable and sustainable
- Resistant to abrasion and wear
Technical Specifications and Grades of Stainless Steel Cast Fittings
Stainless steel cast fittings come in various grades and compositions, each suited for specific applications. The following tables summarize the most commonly used grades and their specifications.
Stainless Steel Cast Grades and Composition
| Austenitic Stainless Steel Casting Grades | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 | 304 | 304L | 316 | 316L | 347 | 317 | ||
| Silicon | Min-Max | 2.0 Max | 2.0 Max | 2.0 Max | 2.0 Max | 1.5 Max | 2 Max | 1.5 Max |
| Manganese | Min-Max | 1.5 Max | 1.5 Max | 1.5 Max | 1.5 Max | 1.5 Max | 1.5 Max | 1.5 Max |
| Carbon | Min-Max | 0.16 Max | 0.08 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.08 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.08 Max | 0.08 Max |
| Chromium | Min-Max | 18.0 - 21.0 | 18.0-21.0 | 17.0-21.0 | 18.0-21.0 | 17.0-21.0 | 18.0-21.0 | 18.0-21.0 |
| Nickel | Min-Max | 9.0-12.0 | 8.0-11.0 | 8.0-12.0 | 9.0-12.0 | 9.0-13.0 | 9.0-12.0 | 9.0-13.0 |
| Phosphorus | Max | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Molybdenum | Min-Max | 0.40-0.80 | 2.0-3.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 3.0-4.0 | |||
| Sulfur | Min-Max | 0.20-0.40 | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel Casting Grades | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 409 | 442 | 446 | |||
| Carbon | Max | 0.16 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |
| Silicon | Max | 2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Manganese | Max | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | |
| Nickel | Max | 0.5 | 2 | 4 | |
| Chromium | Min-Max | 10.5-11.75 | 18.0-22.0 | 26.0-30.0 | |
| Molybdenum | Max | ||||
| Sulfur | Max | 0.045 | 0.04 | 0.04 | |
| Phosphorous Max | 0.045 | 0.04 | 0.04 | ||
| Copper | Max | ||||
| Martensitic Stainless Steel Casting Grades | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 416 | 410 | 15-5 PH | 420 | 17-4 PH | ||
| Silicon | Min-Max | 1.50 Max | 1.5 Max | 0.50-1.00 | 1.0 Max | 0.50-1.00 |
| Carbon | Min-Max | 0.15 Max | 0.05-0.15 | 0.05 Max | 0.15 Max | 0.06 Max |
| Manganese | Max | 1.25 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.7 |
| Nickel | Min-Max | 0.50 Max | 1.0 Max | 4.20-5.00 | 3.60-4.60 | |
| Chromium | Min-Max | 11.5-14.0 | 11.5-14.0 | 14.00-15.50 | 12.0-14.0 | 15.5-16.7 |
| Phosphorous | Max | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.025 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Molybdenum | Min-Max | 0.50 Max | 0.5 Max | |||
| Copper | Min-Max | 0.50 Max | 0.50 Max | 2.5-3.2 | 2.8-3.5 | |
| Sulfur | Min-Max | 0.15-0.35 | 0.04 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.03 Max |
| Duplex Stainless Steel Casting Grades | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A890 Grade 4A (CD3MN) | ASTM A890 Grade 1A (CD4MCu) | ||
| Carbon | Max | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Silicon | Max | 1 | 1 |
| Molybdenum | Min-Max | 2.5-3.5 | 1.75-2.25 |
| Chromium | Min-Max | 21.0-23.0 | 24.5-26.5 |
| Manganese | Max | 1.5 | 1 |
| Nickel | Min-Max | 4.5-6.5 | 4.75-6.00 |
| Phosphorous Max | 0.04 | 0.04 | |
| Copper | Min-Max | 1.00 Max | 2.75-3.25 |
| Sulfur | Max | 0.02 | 0.04 |
Testing Requirements for Stainless Steel Precision Casting
To ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of stainless steel castings, testing is essential. These tests help identify potential issues before they become costly problems. Below are the standard testing methods for ASTM A351 CF8M cast fittings:
ASTM A351 CF8M Cast Fittings Testing Methods
- Mechanical Testing
- Hardness Test
- Tensile Test
- Impact Test
- Visual Inspection
- Chemical Composition Analysis
- Dimensional Inspection
- Ultrasonic Testing
- Radiographic Testing
Types of Stainless Steel Pressure Die Casting Processes
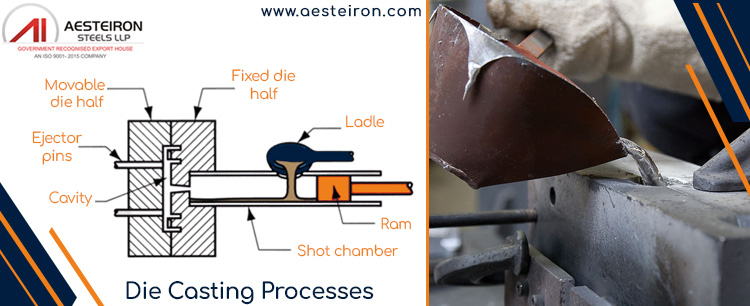
Pressure die casting is divided into two main types:
High Pressure Die Casting
- Divided into two halves, mounted on plates.
- One part is fixed to a stationary plate, the other to a movable plate.
- Used for high-speed injection, up to 1100 bar.
- Includes cold chamber and hot chamber methods.
- After solidification, the die opens automatically to release the casting.
Low Pressure Die Casting
- Produces high-quality castings with less defect risk.
- Used for metals with lower melting points (not ideal for stainless steel).
Methods Used for Stainless Steel 316 Casting
| Methods | |
|---|---|
| Investment Casting | Uses wax or foam patterns to create detailed molds. |
| Sand Casting | Utilizes sand molds for complex and accurate components. |
| Continuous Casting | Used for industrial production of continuous lengths of stainless steel. |
| Pressure Die Casting | Creates near-net-shape designs with high-end metal castings. |
| Centrifugal Casting | Used for filling molds through centrifugal force. |
| Corner Casting | Designed to produce corner-shaped castings. |
| Lost Wax Casting | A process where the wax pattern is removed after casting. |
SS Investment Casting vs Sand Casting
| Features | Stainless Steel Investment Casting | Sand Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High melting point alloys (e.g., stainless steel) | Low to medium-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, zinc) |
| Surface | Smooth finish, often ready for use. | Coarser finish, usually requires additional finishing. |
| Mechanical Properties | Excellent mechanical properties and strength. | Good mechanical properties, but not as strong as investment casting. |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision and tight tolerances. | Lower precision and looser tolerances. |
| Complexity | Capable of producing highly intricate and detailed shapes. | Best for simpler and less complex parts. |
| Tooling | Expensive initial tooling, but reusable. | Relatively low-cost tooling, often single-use. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to detailed patterns and materials. | Lower cost due to simpler patterns and materials. |
| Application | Used in aerospace, medical, and high-precision industries. | Common in general manufacturing and large industrial parts. |
Steel Wire Spiral Hydraulic Hose
High pressure and pulse resistance and long service life, Letone steel wire spiral Hydraulic Hose fully meets the needs of high-end hose users such as heavy machinery and equipment manufacturers. Letone hydraulic hose is guaranteed for use in the construcion, mining, agriculture, oil & gas and other industries with high performance.
Steel Wire Spiral Hydraulic Hose,Rubber Hose,Spiral Hose,Steel Wire Hose
Luohe Letone Hydraulic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.litonghose.com